CleanTech
Cleantech companies in the East Bay are defining the industry by both small and large companies alike. Driven by younger, mission-driven, and talented entrepreneurs seeking to combat climate change, these companies are developing transformative products and technologies to solve the world's greatest environmental and resource challenges. Building on technology breakthroughs from universities, government, and venture capital, the cleantech industry is evolving rapidly.

Why the East Bay?
Startup Culture
- Highly creative and mission-driven companies
- Diverse and inclusive workforce
- Growing venture capital activity
- Collaborative resource and knowledge sharing
Space to Grow
- Supportive business climate
- Flexible industrial supply
- Access to academic and research institutions
- Growing network of incubators and accelerators
INDUSTRY SUMMARY
Description
The cleantech manufacturing industry is very diverse and encompasses a wide range of companies and activities, ranging from renewable energy (solar, wind, water, and biofuels), green building and transportation, to waste and resource management. Due to the multifunctional nature of companies’ operations, many cleantech manufacturers are engaged in R&D and engineering and consulting services.
Although the cleantech industry remains nebulous, the East Bay is driving innovation and investments in California and the nation. The industry is rapidly evolving as new technologies, processes and systems are developed by East Bay companies to solve the world’s most pressing environmental challenges.
This sector is represented by over 100 companies in the East Bay ranging from startups to mid-sized tech companies ready to scale and commercialize. Many companies are engaged in R&D and manufacture locally, while some larger companies will perform contract manufacturing elsewhere. Click here to view East Bay cleantech companies.
Autotech, led by Tesla and other EV tech companies located in the East Bay, is also driving major investments and breakthroughs in the cleantech ecosystem.
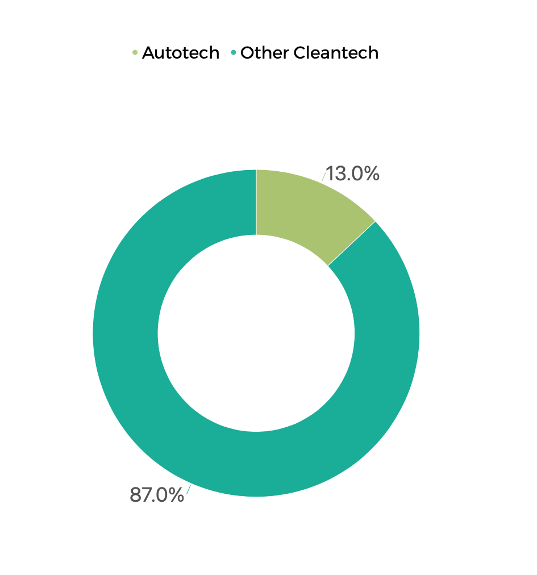
Number of Companies in Autotech and Other Cleantech, 2023
East Bay cleantech geography is predicated on the needs of companies at different stages of their development. Companies in the early stage of their technology life cycle tend to cluster near research institutions, national labs, and other tech companies to get access to science, talent, and lab space. More mature companies move to locations with prototype lab opportunities and sufficient infrastructure.
The location for the companies that are ready to manufacture depends on how they scale up, either via in house manufacturing or contract manufacturing. Companies scaling in house usually locate in cities with land and building availability. Thus, there is a particular pattern of movements around the East Bay itself as companies mature and grow from their startup stage. More than 50 percent of cleantech companies, mostly startups, are in Berkeley. Another 30 percent are in Fremont, Hayward, and Livermore.
“It is the right place to actually engage community, especially at the heart of where environmental justice really plays into our climate future.”
100+
Cleantech companies in the East Bay
Key Players
This sector is characterized by a diversity of companies based on their technological scope, years in operation, and customer base. Many small startups focusing on one technology emerged within the last decade. Companies with ten years in operation or longer constitute the group of mid-size producers in active manufacturing mode. Automotive companies are among the largest based on revenues and number of employees.
Major cleantech players include Sila Nanotechnologies, Natel Energy, Clarity Movement, Sunpower Corporation, and Tesla.
Cleantech is evolving as innovation and synergies happen. Part of the change is attributed to more traditional manufacturers innovating from within, for example, the automotive manufacturing segment turning into autotech. The accelerated growth and the reputation for innovation of this industry, though, is largely attributed to entrepreneurial activities in newly developing sectors addressing climate change challenges both directly and indirectly. Cleantech “activities” are occurring across many different industries, including but not limited to agriculture, biotech, energy production and storage, PSTS (professional, scientific and technical services), and transportation.
The nature of the cleantech industry is changing as well. East Bay companies are positioning themselves as a part of the global value chain, as they focus on one aspect of global cleantech. In addition, cities introduce incentives and lower entry barriers for new companies willing to relocate. Thus, specialization happens on the city level as well as on the regional level.
On the regional level, a cleantech cluster can position itself as Cleantech East Bay and competes as such not only on the national but also international level. When it comes to the needs of individual companies, however, each subsegment of cleantech poses segment-specific challenges and opportunities. The battery producers, for example, make up their own micro-climate with their own sector dynamics such as a high growth rate supported by legislation and incentives for the decarbonization of the local economy.

Number of Jobs
As mentioned, cleantech manufacturing spans across many industries therefore it is unclear how many jobs this sector actually represents. According to an analysis of 14 NAICS codes, the cleantech manufacturing accounts for approximately 25,000 jobs and has seen significant growth in the last decade. There be thousands of additional jobs associated with cleantech, such as positions in management, R&D, and engineering services among other services.
6-NAICS used in this analysis: 221111, 221114, 221115, 221116, 221117, 333413, 333611, 334512, 334515, 335311, 335910, 336110, 336120, 336211.
The labor market for the East Bay cleantech industry is characterized by fierce competition in hiring. The supply of jobs in the East Bay is six times the national average. The East Bay also outpaces the nation in terms of average earnings and job postings.
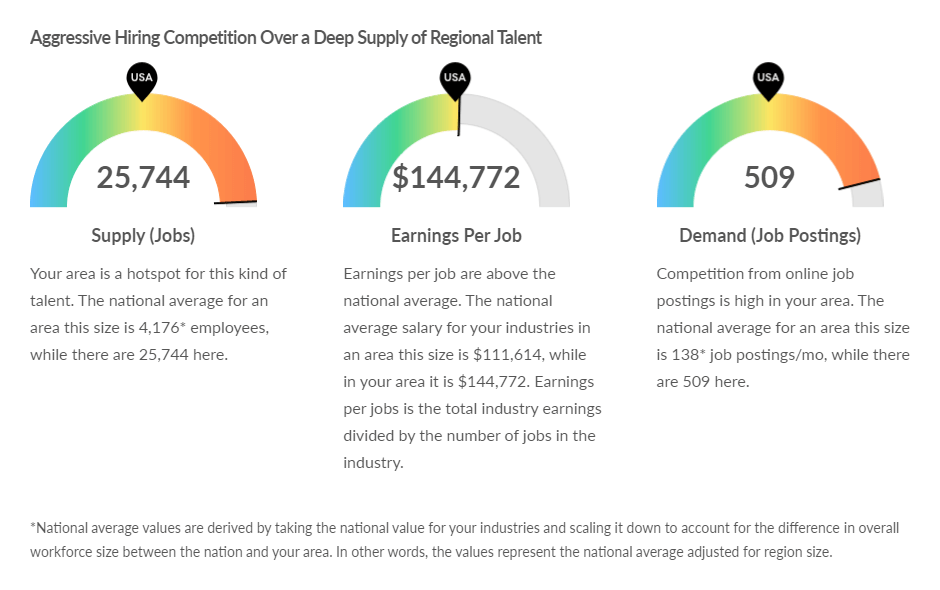
Hiring Competition in Cleantech Industry, Alameda and Contra Costa Counties, Lightcast, 2023
Current job postings are skewed by labor demands in the automotive industry with Tesla and Lucid Motors advertising for the majority of jobs in this sector. The three top skills required are in global supply management, equipment maintenance, and manufacturing engineering. In general, manufacturing and production jobs often do not command advanced degrees and offer apprenticeships and on-the-job-training.
Trends and Driving Force
Clustering of cleantech companies creates a favorable condition for the development of the entire ecosystem that spans several industries and thrives on the culture of innovation and collaboration.
The sector growth is fueled by new technology development, advancement in manufacturing, and construction of support infrastructure, especially to support the fast-growing market for electric vehicles. Greentech, which focuses directly on improving environmental quality, is the subsector of cleantech that is the most robust in the East Bay and is poised to continue growing as society transitions towards sustainability and energy independence.
Industrial space availability will continue to be a factor for growth within the region. The East Bay currently is able to meet the space and expansion needs of cleantech companies at every stage of companies’ life cycle. Proximity to national labs and incubator-type facilities allows for support at the early technology development stage. Pilot line production is often set up in existing buildings with well-developed electricity infrastructures, but as companies come to full scale manufacturing they may choose to retrofit or to develop new land and property. Thus, cleantech companies are often on the move, expanding real estate footage for offices, R&D labs, and production.
“Compared to SF, there is significantly more space to be had in the East Bay.”
Part of the cleantech industry growth comes from expanding its customer base beyond the East Bay. Also, growth is fueled not only by geographies but by vertical product integration, especially for those East Bay companies that are starting to manage value chains in global markets. East Bay cleantech would benefit from regional collaborations and an institutional body at the regional level to lobby for industry’s interests nationally and in the global arena.

Challenges and Opportunities
In Spring 2023, East Bay EDA convened focus groups and interviews with industry leaders who shared why they’ve chosen to locate and invest in the East Bay, as well the challenges and opportunities facing the industry.
Challenges
Companies report limited access to resource sharing that is also industry specific. This includes information on funding and grant opportunities at the city, state, and federal levels, access to tools that help with decision-making onsite selection, support with tenant-owner relationship, and city permitting.Companies report the need for industry specific network opportunities that would include access to platforms for finding partners and collaborators. Community building was mentioned as a challenge as companies focus on immediate needs rather than the collective needs of the sector.
“And having the opportunity to be able to talk to people in person at different events that are going on around the Bay is the best recruiting tool that you can have.”
Opportunities
The companies plan to scale up operations through equipping and launching production lines, moving into bigger spaces, retrofitting existing properties, and developing new factories as well as determining optimal locations for manufacturing facilities over the next 1-2 years. In terms of companies capturing these opportunities, two themes have emerged:
Cleantech is a very dynamic sector represented by mission-driven professionals in science and engineering who exhibit the spirit of cooperation and are willing to share experiences and resources. This spirit of cooperation and the shared goal that goes beyond profit generation is why many opt to start and remain in the East Bay. Community support, culture of nurturing startups, and quality of life and outdoor activities are all enablers for growth. Proximity to similar companies and the availability of funds, and access to space for every stage of company’s lifecycle creates a network of resources that fuels the culture of innovation.
“We are very outdoorsy company too, so a lot of people bike to work. Our bike racks are just constantly piled up.”
Many companies in the cleantech space are engaged in systematic change looking to improve not only their product, but also to initiate a mind shift.
The reality is that the markets are not ready for a rapid change. In many cases, unless end users are required to implement changes by legislation, they do not necessarily drive demand for sustainability.
It is on cleantech companies to demonstrate the economics and rational for their new improvements to end-users. Heavy science-based cleantech companies have longer time to market and a higher failure rate.
Being business smart is what is required of cleantech companies. In the environment in which the track record of success for new products does not yet exist and the adoption rates are slow, companies need to come up with new creative business models that work for their customers.
A simple question of who benefits from new technology and how helps the cleantech industry implement incremental changes in their customers’ processes rather than systemic disruptions of established practices.
Also, finding partners within the value chain who can help you scale up through their existing structures becomes a crucial factor of a successful launch.
Recommendations & Future Opportunities
When asked what industry most needed from regional and local partners, stakeholders shared their top recommendations.
Collaboration Platform: Examples include leadership networking forums to share experiences and industry-specific resources.
Property Search Tool: Inventory of locations for local company expansion.
Business Support: A central resource hub containing information on access to capital, programs and resources. Cleantech companies also need assistance with local permitting and streamlined processes, e.g., hazardous waste permitting and handling, utilities, and other needs.




